
The transportation sector is one of the key sectors of current and future energy consumption in China. The low-carbon green transformation of the transportation industry is crucial for China's low-carbon development, especially the goal of achieving the carbon contribution before 2030. In the context of China's energy shortage and climate change, there is an urgent need to curb the energy needs of the future transportation sector and reduce its carbon emissions to promote the sustainable development of the transportation sector. However, the layout of the energy technology development path of the transportation sector is not only very complicated but also has great uncertainty. Therefore, this study predicts the future intercity transportation demand and transportation structure by constructing the C3IAM/NET-Transport model and then elaborates on the various energy technologies that provide intercity transportation services. On this basis, with the minimum total cost as the optimization goal, the competition and substitution relationship between transportation energy technology is visually depicted, and the corresponding energy consumption and emissions are simulated under different policy scenarios to support the formulation of green development goals in the transportation sector in the future.
The results show that the total demand for intercity passenger transport in China will grow steadily in the long run, among which private transportation will be the main growth point, and the intercity passenger transport structure will shift to the transportation mode of high carbon emissions. The development of high-speed railway can restrain the demand for air travel to some extent, which will optimize the intercity passenger travel structure. The study also found that in 2050, China will face 6.0 to 9.1 trillion kilometers of intercity passenger transportation demand, as well as 6.6 trillion kilometers of intercity private transportation needs. Without taking any measures to meet passenger demand, the total energy consumption and CO2 emissions of China's intercity passenger transport sector will continue to grow in the future, reaching 456 million tons of standard coal and 873 million tons of emissions by 2050. Based on the relevant results, this study proposes that the energy efficiency of transportation equipment should be promoted, the passenger transport structure should be optimized, and the use of new energy should be promoted, so as to reverse the rising trend of carbon dioxide in the intercity passenger transport sector and reach a peak emission of 489 million tons of CO2 by 2030.
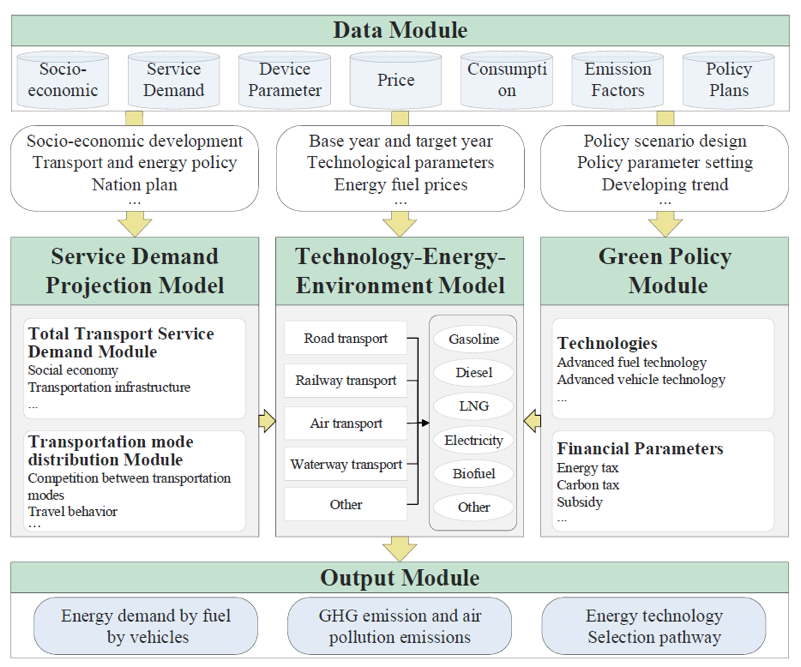
The C3IAM/NET-Transport model framework
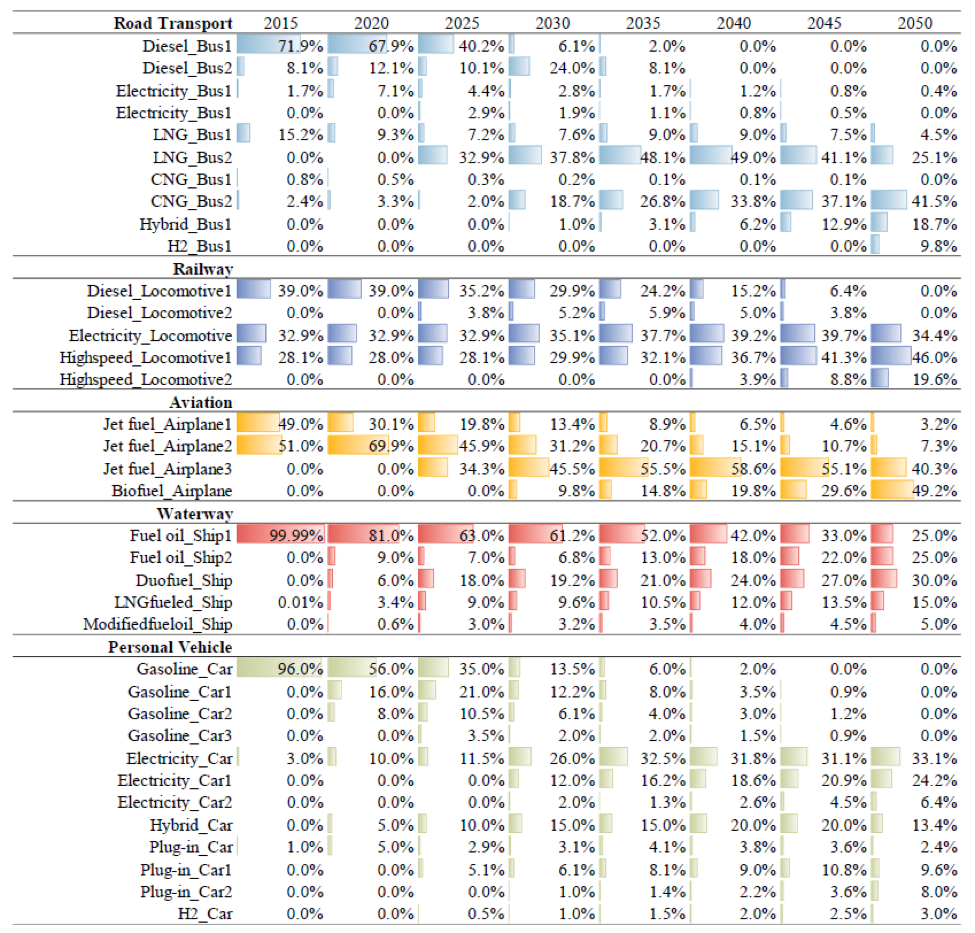
Vehicle fuel and technology development pathway for intercity passenger transport under the SD Scenario
Bao-Jun Tang, Xiao-Yi Li, Biying Yu and Yi-Ming Wei (2019), Sustainable development pathway for intercity passenger transport: A case study of China, Applied Energy.
Original information:Sustainable development pathway for intercity passenger transport: A case study of China
Original link:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113632